Unveiling the Fact Behind Sugar Beet Vs Sugar Cane: Advantages, Utilizes, and Processing Techniques Explained
The difference between sugar beet and sugar cane is often forgotten in discussions concerning sugar production. Each crop provides one-of-a-kind benefits and applications in various markets. Their growing methods and handling techniques likewise vary significantly. Recognizing these subtleties is necessary for stakeholders in the sugar sector. What effects do these differences have for wellness, taste, and environmental influence? Checking out these aspects can reveal much deeper understandings into the international sugar market.
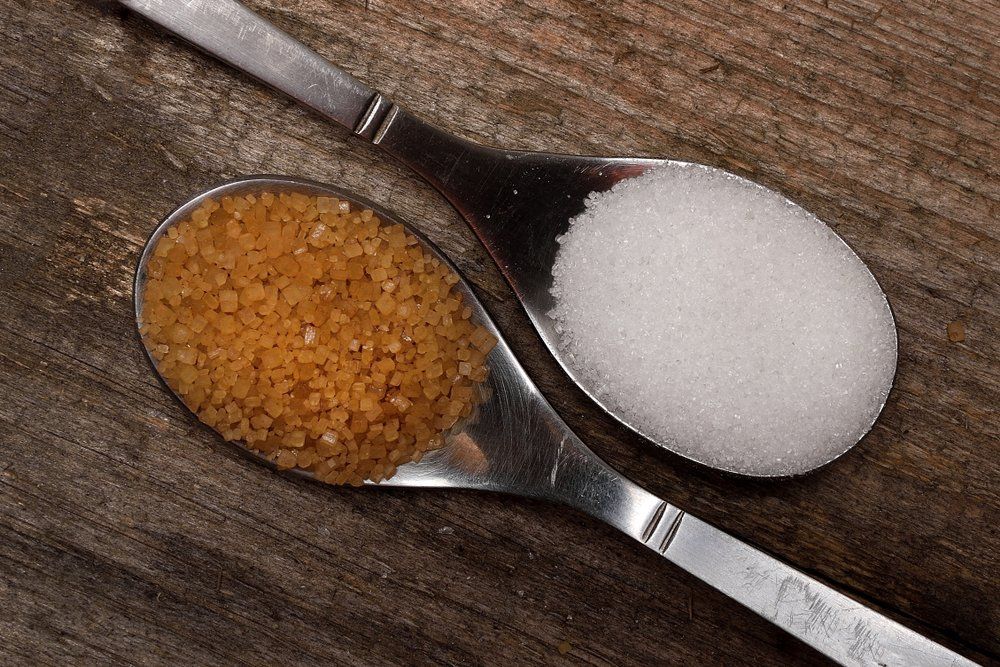

Summary of Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane
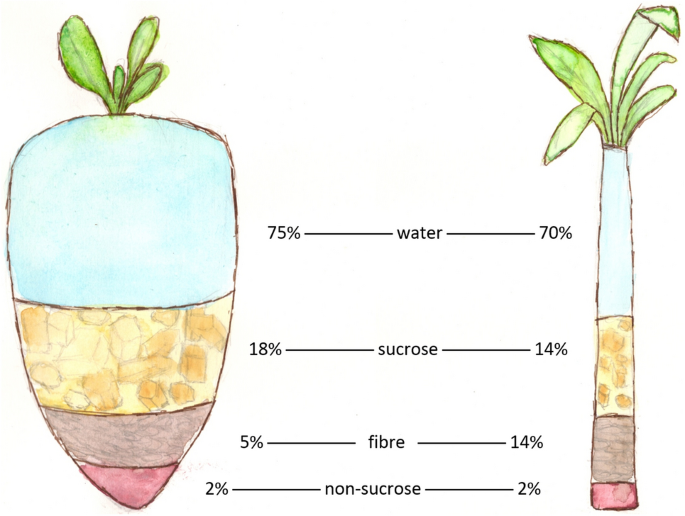
Sugar beet and sugar cane are two main resources of sugar, each with distinct attributes and growing methods. Sugar beet, an origin veggie, grows in warm climates and is commonly gathered in the loss. Its high sugar material, varying from 15% to 20%, makes it a beneficial crop for sugar manufacturing. The process includes drawing out juice from the beetroots, which is after that fine-tuned into granulated sugar.
In contrast, sugar cane is an exotic turf that flourishes in warm, damp settings. It can accomplish a sugar content of as much as 14%, yet its tall, fibrous stalks need considerable processing. The cane is squashed to remove juice, which undergoes boiling and formation to produce sugar. Both sources add considerably to the global sugar supply, with sugar beet mainly grown in Europe and North America, while sugar cane is chiefly grown in Brazil, India, and other exotic regions.
Cultivation Practices: Sugar Beet vs. Sugar Cane
Farming practices for sugar beet and sugar cane differ considerably because of their distinct growing conditions. Sugar beetroots flourish in cooler environments with well-drained soil, while sugar cane likes warmer temperatures and plentiful moisture. Additionally, the harvesting strategies used for every crop mirror these ecological demands and affect general return and high quality.
Growing Conditions Contrast
While both sugar beet and sugar cane thrive in particular ecological problems, their farming practices vary markedly. Sugar beet is mostly grown in warm regions, preferring cooler environments with well-drained soil and moderate rains. It calls for an expanding period of about 90 to 120 days, with suitable temperatures between 15 ° C to 25 ° C. On the other hand, sugar cane embellishments in exotic and subtropical environments, growing in warm temperatures varying from 20 ° C to 32 ° C. It calls for abundant sunshine and consistent rainfall, often requiring watering in drier locations. Sugar cane has a much longer growing cycle, typically lasting 12 to 24 months. These distinctions in expanding problems significantly affect the geographical distribution and farming practices connected with each crop.
Collecting Techniques Differences
The harvesting strategies for sugar beet and sugar cane reflect their distinct development features and agricultural techniques. Sugar beet is generally collected mechanically, with harvesters made to uproot the whole plant, guaranteeing marginal soil disruption. The beetroots are then delivered for processing quickly after harvest to preserve high quality. On the other hand, sugar cane harvesting typically entails a mix of handbook and mechanical approaches. Employees might initially cut the cane by hand, especially in regions where automation is less practical. Subsequently, specialized machinery is employed to collect and transport the cut stalks to refining facilities. These varying methods not just impact performance but additionally affect the high quality and yield of the last sugar products, showcasing the flexibility of each crop to its setting.
Nutritional Contrast and Wellness Benefits
When contrasting the dietary profiles of sugar beet and sugar cane, it becomes clear that each deals distinctive health and wellness benefits. Sugar beetroots are abundant in crucial nutrients like folate, manganese, and potassium, which add to total wellness. They likewise contain fiber, which helps food digestion and might assist control blood sugar levels. In addition, sugar beets are known for their antioxidant properties, which can combat oxidative anxiety.
Alternatively, sugar cane is primarily made up of sucrose, giving fast energy. While it lacks the same degree of nutrients discovered in sugar beets, sugar cane does consist of little amounts of B nutrients such as calcium and magnesium. Sugar cane juice is often proclaimed for its hydrating properties and prospective health and wellness benefits, consisting of improved digestion health. Eventually, the option between sugar beet and sugar cane may depend upon private wellness objectives and nutritional preferences.
Taste Profiles and Culinary Uses
Taste profiles of sugar beet and sugar cane vary considerably, influencing their culinary applications (Sugar beet vs sugar cane). Sugar cane, with its normally sweet and complex taste, is usually favored in beverages, treats, and different cooking recipes. It lends a rich, caramel-like note that improves the taste of products such as syrups, molasses, and rum. On the other hand, sugar beet has an extra neutral and less fragrant preference, making it appropriate for applications where sweet taste is preferred without altering the dish's fundamental flavors. It is frequently used in refined foods, baked products, and sugar
Culinary specialists commonly pick sugar cane for its depth and splendor, especially in premium food preparation and craft beverages. On the other hand, sugar beet's adaptability as a sugar in mass-produced things caters to a broader market. Inevitably, the selection in between these two sugars can considerably influence taste accounts and total culinary experiences.
Ecological Influence of Sugar Production
Sugar manufacturing, whether from sugar beet or sugar cane, brings significant environmental implications. Sugar cane growing often results in deforestation, particularly in tropical areas, disrupting regional communities and adding to biodiversity loss. The comprehensive use fertilizers and pesticides in both sugar beet and sugar cane farming can cause soil destruction and water air pollution, affecting surrounding environments and communities. Furthermore, the high water usage needed for sugar cane watering presents a threat to local water products, specifically in deserts.
Alternatively, sugar beet go to these guys farming commonly takes place in temperate climates, which might minimize some deforestation problems. However, it is not without its very own obstacles, including soil erosion and dependence on chemical inputs. In general, the ecological effect of sugar manufacturing is multifaceted, necessitating lasting farming techniques and recognition of resource monitoring to lessen damages to ecological communities and promote environmental wellness.
Processing Techniques: From Plant to Sugar
Countless processing strategies are used to transform sugar beet and sugar cane into granulated sugar, each approach reflecting the one-of-a-kind characteristics of the source plant. For sugar beets, the procedure begins with washing and slicing the roots right into slim strips, which are after that based on diffusion-- a strategy where hot water extracts sugar from the beet slices. The resulting liquid is purified, concentrated, and taken shape.
In comparison, sugar cane handling includes crushing the stalks to remove juice, adhered to by clarification to remove impurities. The juice is after that evaporated, causing syrup that goes through formation. Both processes are followed by separation of the sugar crystals from the molasses, which is a by-product. The lasts consist of drying get redirected here out and packaging the granulated sugar for circulation. These techniques highlight the distinct paths where these two plants produce sugar, each with its very own set of difficulties and efficiencies.
Financial Elements of Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Industries
The economic landscape of the sugar beet and sugar cane sectors discloses significant differences in production prices, market dynamics, and local impacts. Sugar beet, primarily expanded in warm climates, frequently incurs higher production costs because of labor and input expenses. On the other hand, sugar cane flourishes in tropical areas, generally gaining from lower labor prices and favorable weather problems, which can cause higher yields.
Market characteristics also differ, as sugar cane dominates worldwide manufacturing, accounting for roughly 80% of sugar output. This frequency influences pricing frameworks and trade circulations. In comparison, sugar beet is a lot more regionally focused, specifically in Europe and The United States and Canada, impacting local economic situations reliant on beet manufacturing.
Furthermore, changes in global sugar costs can significantly affect both industries, influencing farmer earnings and investment degrees. Comprehending these economic elements is important for stakeholders intending to browse the intricacies of the sugar market successfully.
Frequently Asked Inquiries

Can Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Be Intercropped Effectively?
Intercropping sugar beet and sugar cane offers difficulties as a result of varying development needs and environmental needs. With mindful monitoring and ideal conditions, it might generate advantages such as improved soil health and wellness and resource efficiency.

What Are the Historical Origins of Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane?
The historic beginnings of sugar beet trace back to 18th century Europe, while sugar cane has roots in Southeast Asia, grown for thousands of years. Both plants have actually substantially influenced global sugar manufacturing and farming.
Just How Do Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Affect Dirt Health And Wellness?
The effects of sugar beet and sugar cane on soil health and wellness differ. Sugar beet can improve dirt structure and nutrient web content, while sugar cane you can try this out might deplete nutrients otherwise handled properly, affecting lasting dirt fertility.
Exist Any Type Of Arising Technologies in Sugar Manufacturing?
Emerging innovations in sugar production include accuracy agriculture, progressed hereditary engineering for higher returns, and ingenious removal approaches. These innovations aim to boost effectiveness, minimize environmental impact, and boost the overall sustainability of sugar manufacturing procedures.
What Are the Key Distinctions in Labor Needs for Both Crops?
The crucial differences in labor needs for sugar beet and sugar cane hinge on planting, harvesting, and processing. Sugar beet vs sugar cane. Sugar beet typically demands more mechanization, while sugar cane typically requires more manual work for collecting and refining stages